

Our Science
About Mosliciguat
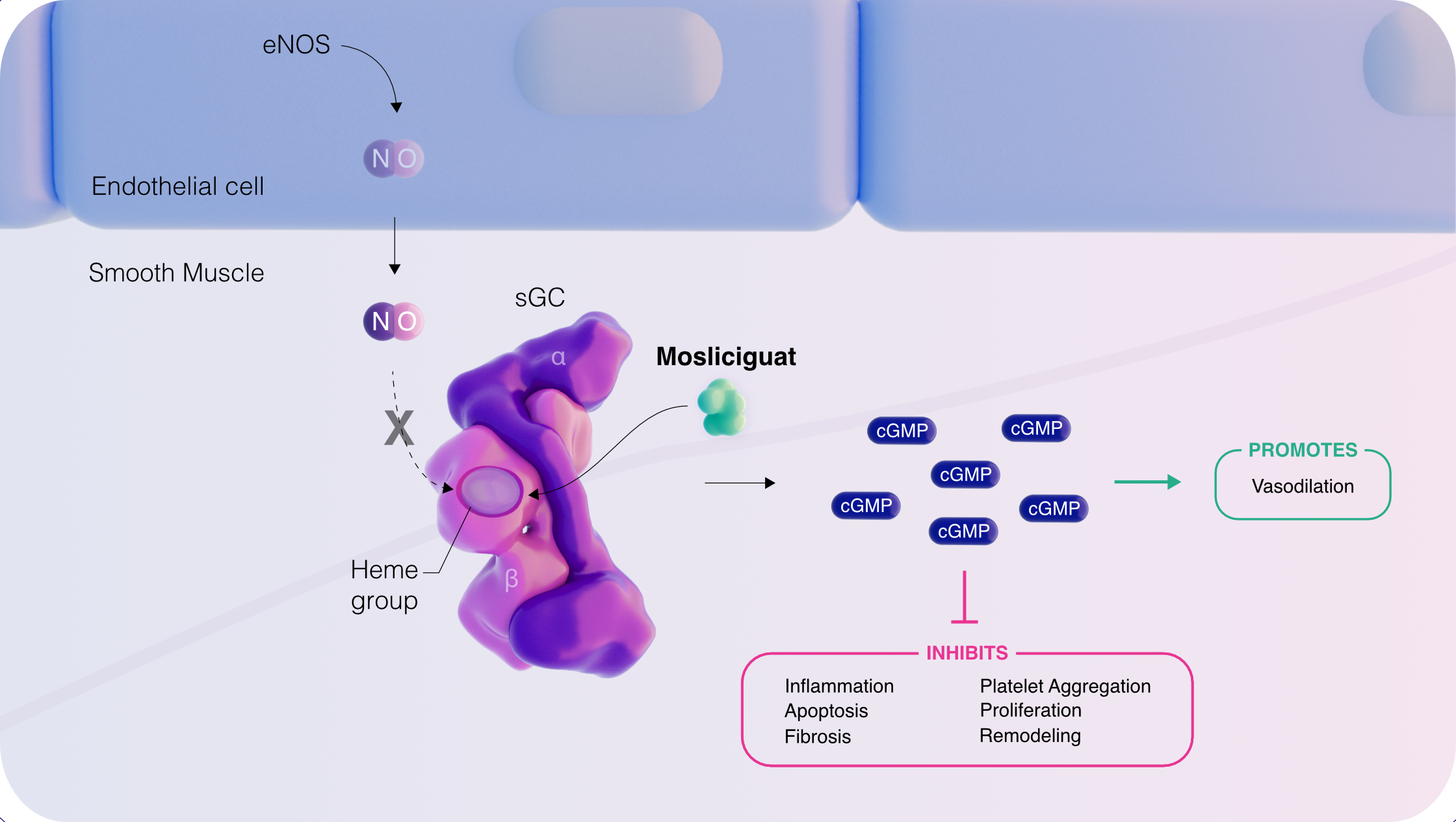
Pulmovant’s first investigational product is mosliciguat, a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) activator. It has the potential to be first-in-class and to have a differentiated mechanism of action (MOA). Mosliciguat’s MOA is thought to drive vasodilation1,2, including in conditions characterized by increased lung tissue hypoxia and oxidative stress3,4 and may have anti-inflammatory5 and anti-fibrotic properties6.
What is sGC?
sGC is a key enzyme in the nitric oxide (NO) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) signaling pathway that helps maintain vascular homeostasis3,4. NO binds the prosthetic heme group of sGC, catalyzing cGMP production, which literature suggests leads to:
- Increased vasodilation1,3
- Reduced inflammation and apoptosis5,7
- Reduced platelet aggregation5
- Reverse vascular remodeling6,7
- Anti-proliferative effects9
- Anti-fibrotic effects7,8
PH and lung disease conditions can have dysfunctional sGC activity10.
Mosliciguat, an sGC activator, aims to restore sGC function, even in conditions of oxidative stress seen in PH-ILD.
- PH and lung disease conditions lead to oxidative stress, which results in less NO and less of the reduced (native) form of sGC and more of the other pathologic variants, such as oxidized and heme-free sGC (Apo) forms4,7,9.
- Mosliciguat, an sGC activator, aims to restore and improve catalytic function of sGC, even the pathological oxidized and heme-free sGC (Apo) variants1,3,4.
- sGC activators mimic NO-bound heme, and therefore are NO-independent and heme-independent1,3,4. This property may allow activators to preserve more sGC enzymatic activity in PH and ILD disease conditions of oxidative stress where there is less NO and less heme1,3.


The inhaled delivery of the drug targets the lungs directly and is intended to improve therapeutic potential while minimizing systemic side effects.
Mosliciguat is currently being investigated in a global Phase 2 trial in pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD).
70 million people live with pulmonary hypertension
What is Pulmonary Hypertension?
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a progressive and debilitating condition characterized by high blood pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs. This elevated pressure forces the heart to work harder to pump blood through the lungs, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and dizziness.6 The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified PH into five groups based on their underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Group 3 PH is a subtype of PH that arises from lung diseases and is the second most common form of PH11-13.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) describes a large group of diseases that causes progressive damage of the lungs, making it difficult for patients to breathe10.
In the US and EU, up to 200,000 patients are living with pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD)14,15, a subset of Group 3 PH, and have limited to no approved treatment options. Current available treatment options require multiple doses per day16 and can be difficult for patients to adhere to.
Mosliciguat aims to provide an effective, once-daily, inhaled treatment option with a favorable tolerability and safety profile to patients with high unmet need and limited to no approved treatment options.
Sources:
1. Becker-Pelster, EM et al. Respir. Res. 2022. Volume: 272, Issue: 23
2. Ghofrani, HA et al. ATMOS, a proof-of-concept trial of inhaled mosliciguat in untreated PAH and CTEPH. European Respiratory Society Congress 2024.
3. Stasch, JP et al. Circulation. 2011. Volume: 123, Issue: 20, Pages: 2263-2273
4. Tawa, M et al. Vasc. Pharm. 2022. Volume: 145
5. Mauersberger, C et al. Nature Cardiovascular Research. 2022. Volume 1, Pages 1174–1186
6. Dumitrascu, R et al. Circulation. 2006. Volume 113, Number 2
7. Benza R, et al. Eur Respir Rev. 2024;33(171):230183
8. Sandner, P et al. Respir Med. 2017. Jan:122 Suppl 1:S1-S9
9. Dasgupta AD, et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2015;97(1):88-102
10. Dhont S, et al. ERJ Open Res. 2022;8(4):00272-2022.
11. Humbert M, et al. Eur Respir J. 2023;61:2200879.
12. Maron BA, et al. Eur Respir J. 2024;64(4):2401344
13. Kovacs G, et al. Eur Respir J. 2024;64(4):2401324
14. Sathananthan, M et al. Chest. 2023. Volume 165, Issue 2
15. Raghu, G et al. Eur Respir J. 2015; 46:1113-1130
16. Tyvaso FDA Prescribing Information
